Huntington Disease Peer Reviewed Article
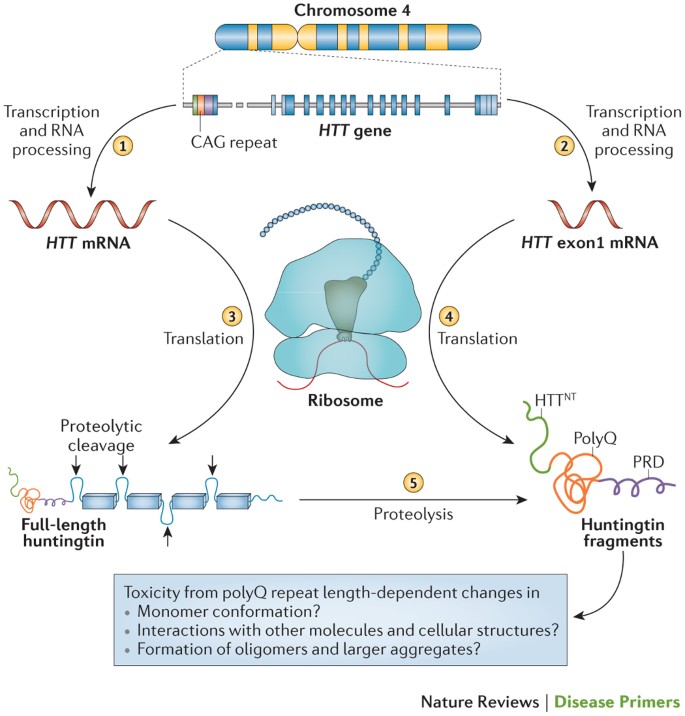
Huntington disease peer reviewed article. Huntingtons disease HD is a fully penetrant neurodegenerative disease caused by a dominantly inherited CAG trinucleotide repeat expansion in the huntingtin gene on chromosome 4. HD is an autosomal dominant neurodegenerative disorder characterized by cognitive deficits psychosis and motor dysfunction Finkbeiner 2011. Parkinsons disease is the most common of several akinetic-rigid syndromes and Huntingtons disease is only one of an ever growing number of trinucleotide repeat disorders.
Huntingtons disease is a devastating inherited neurodegenerative disease characterised by progressive motor cognitive and psychiatric symptoms. Huntington disease is an inherited disease. The Journal of Huntingtons Disease is a peer-reviewed medical journal that will be launched in 2012 and will cover research on Huntingtons disease and related disorders.
To review the existing literature on the prevalence of Huntingtons disease HD in the US and Canada and to estimate the number of people in the US currently affected by this disease. Patients may present with any of these symptoms and familiarity with the phenotype is therefore important. Huntington disease HD is an adult-onset autosomal dominant disorder characterized by progressive deterioration of intellectual function bradykinesia rigidity and progressive chorea.
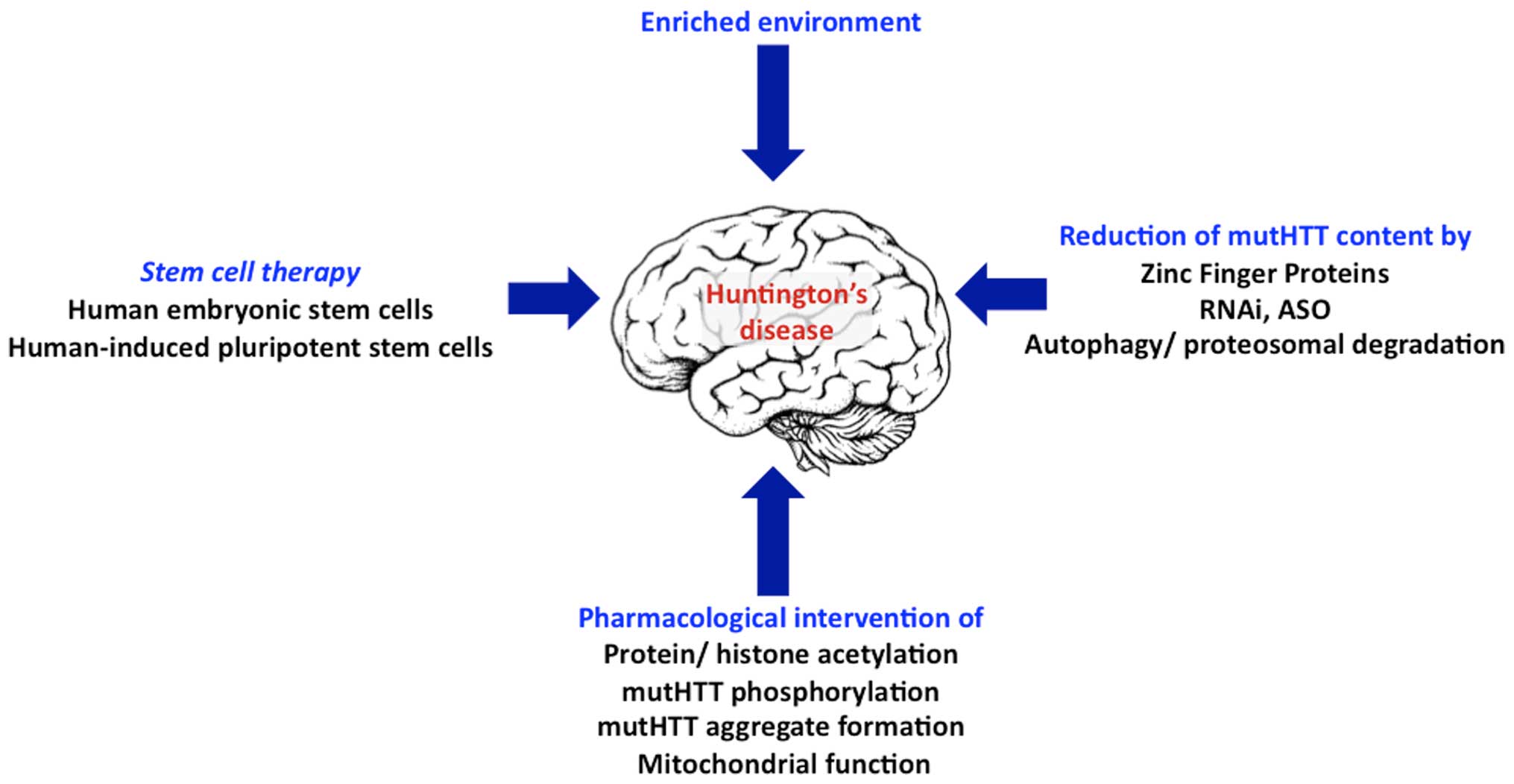
Huntingtons disease HD is a rare neurodegenerative disease of the central nervous system characterized by choreatic movements behavioral disturbances and neuropsychiatric sequelae. HD is a genetic neurodegenerative and ultimately fatal disease. This leads to functional inabilities and psychiatric.
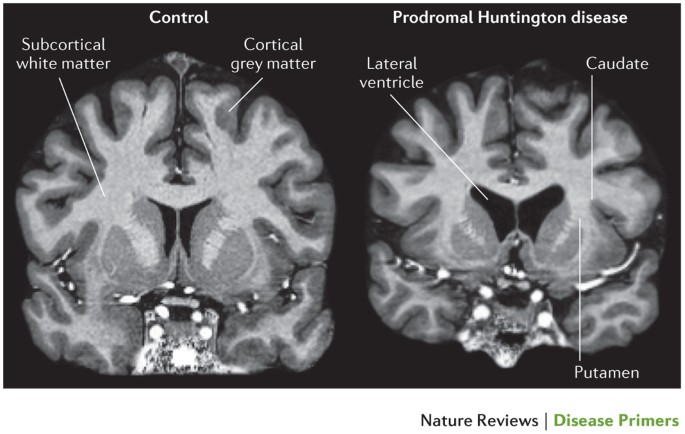
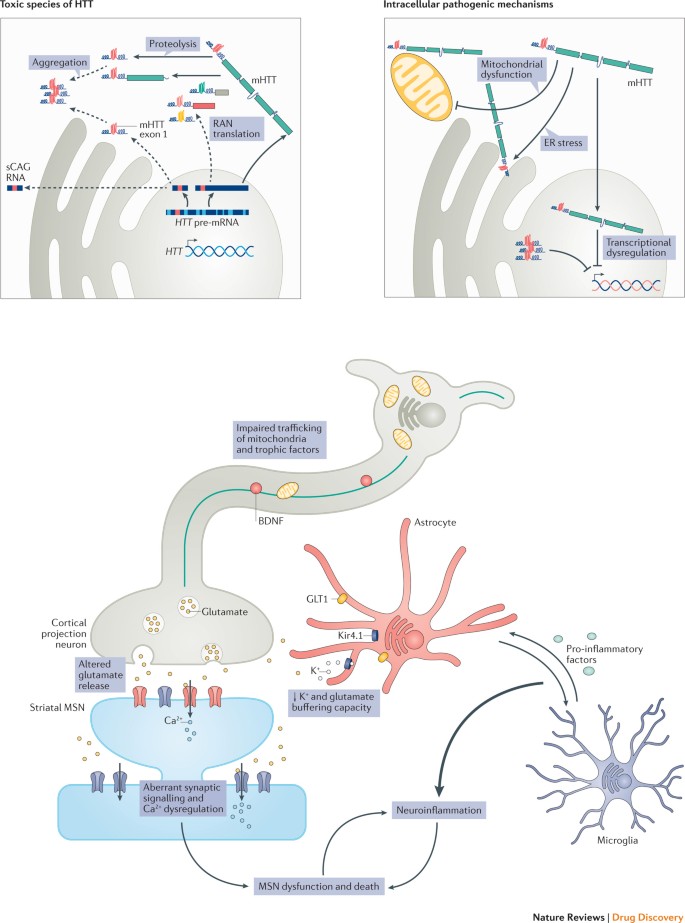
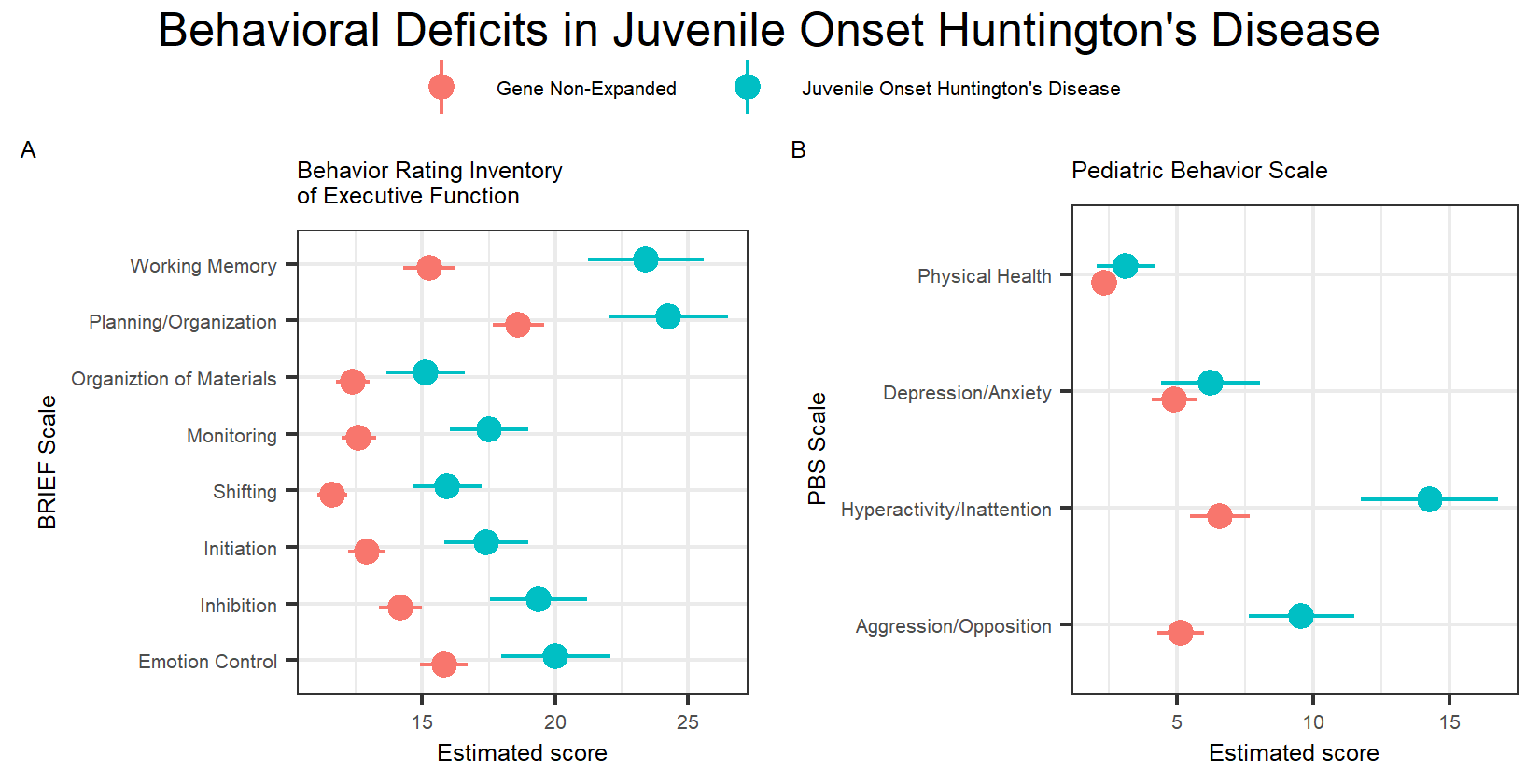
Huntingtons disease HD is a rare autosomal dominant neurodegenerative disorder resulting from expansion of a CAG repeat within the IT15 huntingtin htt gene on chromosome 4p. Mean age at onset of symptoms is 30-50 years. Although it is well established that psychiatric symptoms are common in Huntingtons disease 1-5 research and clinical emphases have been on motor and cognitive aspects of the disorder.
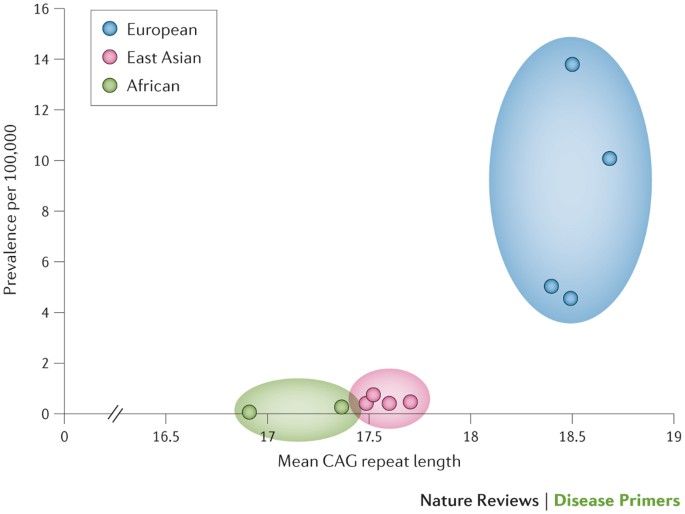
Parkinsons disease and Huntingtons disease are both model diseases. Peer-reviewed journal featuring in-depth articles to accelerate the. Prevalence in the Caucasian population is estimated at 110000-120000.
Sources frequently state that 30000 individuals living in the US have HD but the methodology used to derive this. The disease which gets worse over time attacks motor control regions of the brain those involved with movement as well as other areas.
Huntingtons disease is a devastating inherited neurodegenerative disease characterised by progressive motor cognitive and psychiatric symptoms.
Huntington disease HD is a rare neurodegenerative disorder of the central nervous system characterized by unwanted choreatic movements behavioral and psychiatric disturbances and dementia. Peer-reviewed journal featuring in-depth articles to accelerate the. To review the existing literature on the prevalence of Huntingtons disease HD in the US and Canada and to estimate the number of people in the US currently affected by this disease. Huntingtons disease is a devastating inherited neurodegenerative disease characterised by progressive motor cognitive and psychiatric symptoms. Sources frequently state that 30000 individuals living in the US have HD but the methodology used to derive this. The disease is inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion by an increased number of CAG repeats on the short arm of chromosome 4p163 in the Huntingtin gene. In Western populations HD has a prevalence of 106137 individuals per 100 000. Although it is well established that psychiatric symptoms are common in Huntingtons disease 1-5 research and clinical emphases have been on motor and cognitive aspects of the disorder. Huntingtons disease HD is a rare neurodegenerative disease of the central nervous system characterized by choreatic movements behavioral disturbances and neuropsychiatric sequelae.
The Journal of Huntingtons Disease is a peer-reviewed medical journal that will be launched in 2012 and will cover research on Huntingtons disease and related disorders. Huntington disease HD is an adult-onset autosomal dominant disorder characterized by progressive deterioration of intellectual function bradykinesia rigidity and progressive chorea. Huntington disease causes the degeneration of nerve cells in brain. Parkinsons disease is the most common of several akinetic-rigid syndromes and Huntingtons disease is only one of an ever growing number of trinucleotide repeat disorders. The disease is inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion by an increased number of CAG repeats on the short arm of chromosome 4p163 in the Huntingtin gene. In recent years it has become clear that HD can be regarded as a systemic disorder affecting many organs and tissues causing peripheral as well as brain pathology 2. In Western populations HD has a prevalence of 106137 individuals per 100 000.
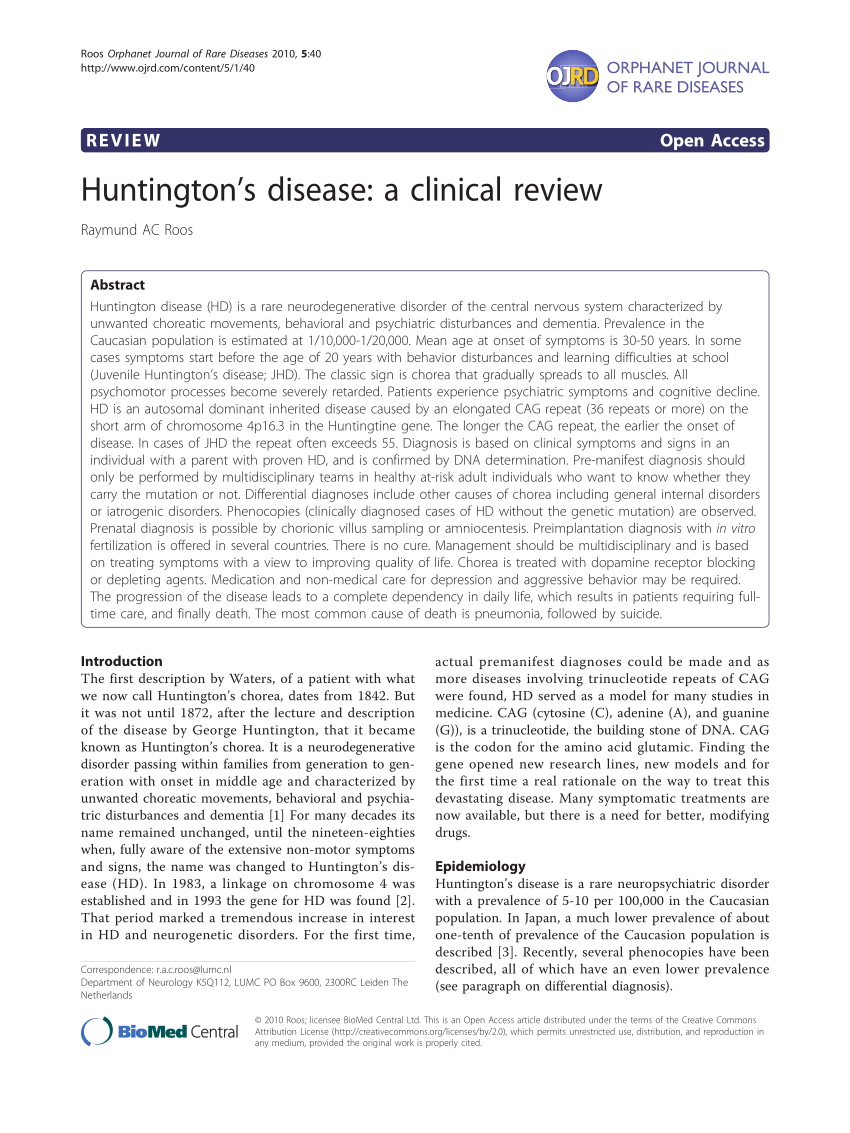
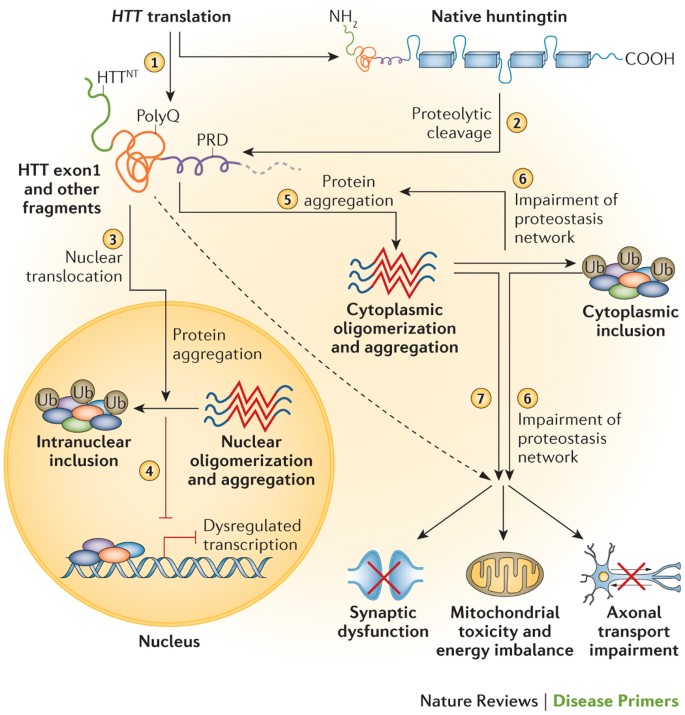

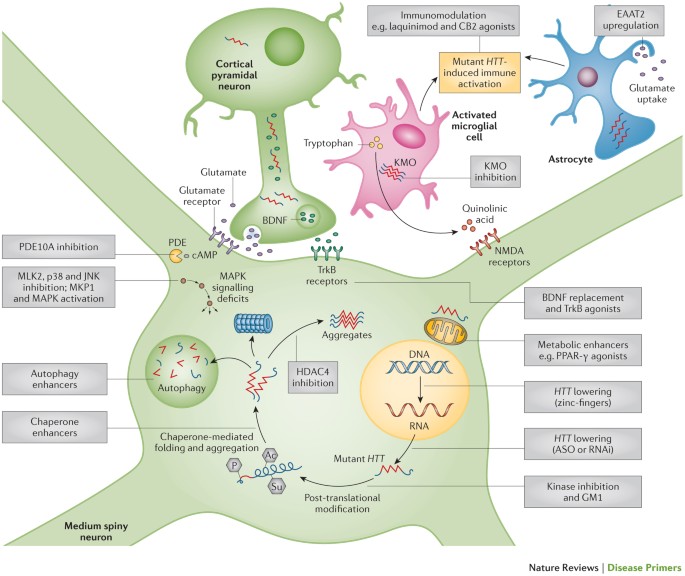






























Post a Comment for "Huntington Disease Peer Reviewed Article"